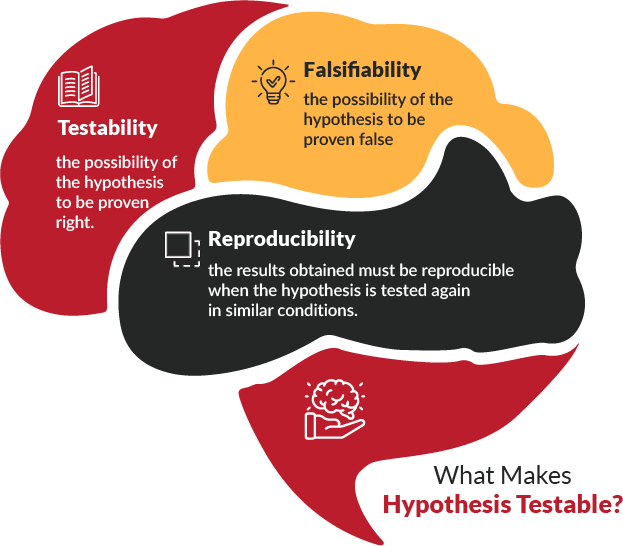
“The relationship between crime statistics and immigration”
This is just another example of a research topic. Do you know what kind of data is required for this particular topic? If not, then find the answer to this question at the end of this blog.
What Is Research Data?
Research data is information that has been collected or observed to test the research hypothesis. Data has to be authentic and reliable in order to conduct a successful and quality research, unreliable data will lead to compromised results. Data can be primary or secondary depending on the requirement of the research that is being conducted.
To select the right type of data that is needed for your study qualitative and quantitative difference. Should be understood. It is also crucial to note that your topic choice leads you to selecting the right data type for your research. A topic that aims to test impact of a certain variable over the other will always be quantitative likewise a topic that aims to analyze a certain variable will be qualitative.
Quantitative vs Qualitative Data
Quantitative data is part of quantitative research. Quantitative research is the use of numbers to collect and present data. For quantitative data the topic should include words like “impact”, “functional relation” and “Effect of” etc. An example of a quantitative topic could be
“To Assess The Impact Of Social Media Marketing On Improving Brand
Awareness In Organizations In Uk”
Qualitative data is based on non-quantifiable elements, it’s more concerned with observations and descriptions. The topic can include terms like “analyze”, “State” and “Understanding” etc. An example of qualitative topic could be
“An Assessment About The Internal Brand Management In Relation To The Issue Of Communication In Employee Engagement – A Case Study Of Pakistan Telecom Industry”
Here’s a chart to help differentiate between quantitative research methods and qualitative research methods:
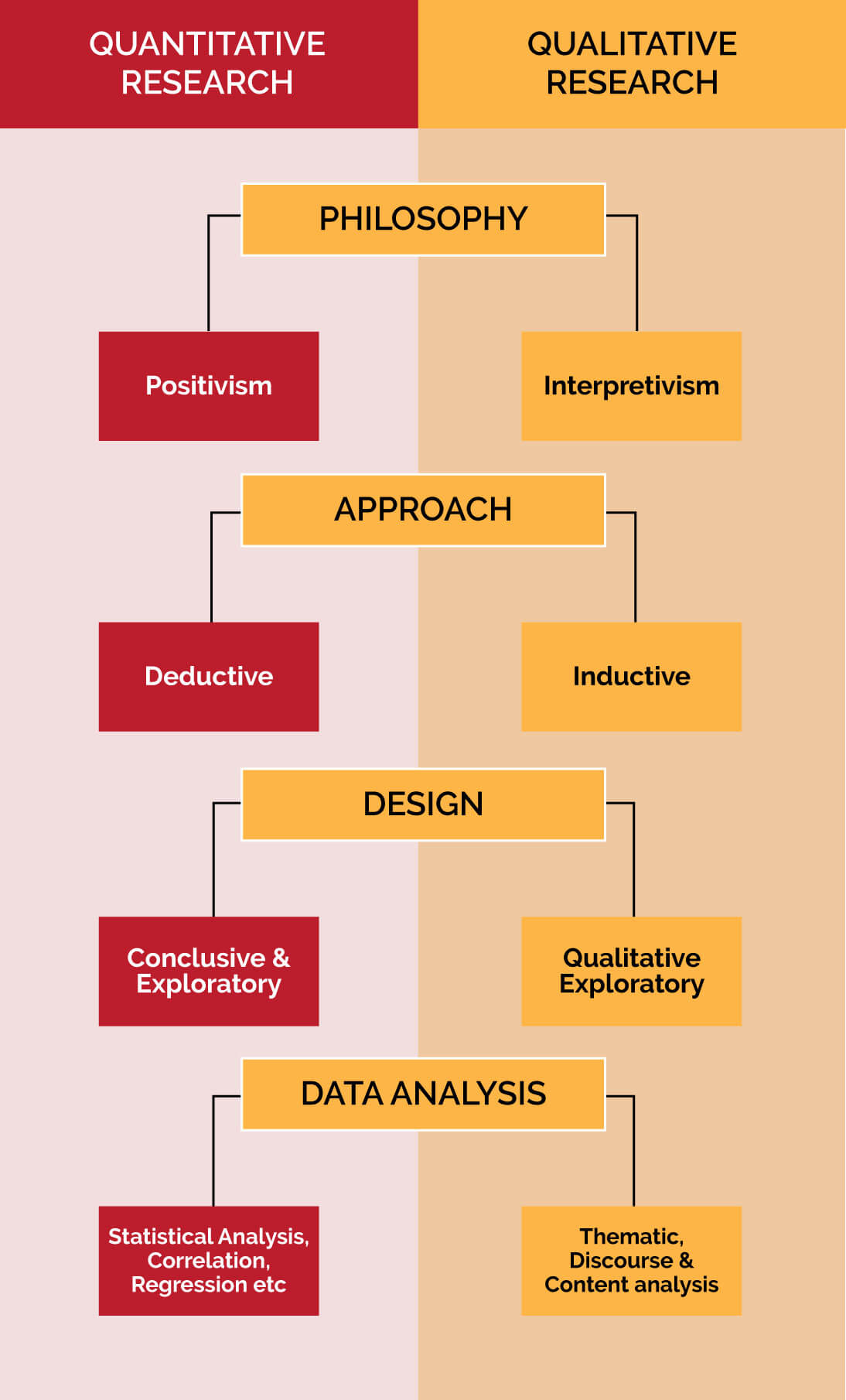
Research philosophy
This defines how you gather, analyze and use the data for your particular research.
In quantitative research we use positivism which tests cause and effect relation whereas in qualitative interpretivism is used which does not test cause and effect relation, it provides the reader with detailed understanding of the topic with different point of views.
Research approach
Deductive approach tests an existing theory and inductive approach helps develop a new theory. In qualitative research inductive approach is followed as qualitative study is for new and innovative topics therefore little to no literature exists. Whereas in quantitative study a theory is tested therefore deductive approach is followed.
Research design
Exploratory research design studies research questions and leaves a gap for further studies on that topic whereas conclusive research design, tests and provides findings for the study and concludes the study. In quantitative research both these approaches can be followed however in qualitative only an exploratory design is implemented.
Data Analysis
To test and analyze the data quantitative study requires to run statistical tests these can include testing the reliability and validity of variables, testing the impact on variables on each other through regression. In qualitative data is analyzed through different methods these include
Thematic Analysis: This is when data is grouped into themes based on their similarities.
Content Analysis: This is when you can identify patterns through the provided data.
Discourse Analysis: This is when you analyze the language, speech or debate. This is mostly conducted to understand cultures.
Depending on your topic and guidelines each of the two, or a mixed data collection method, can be used.
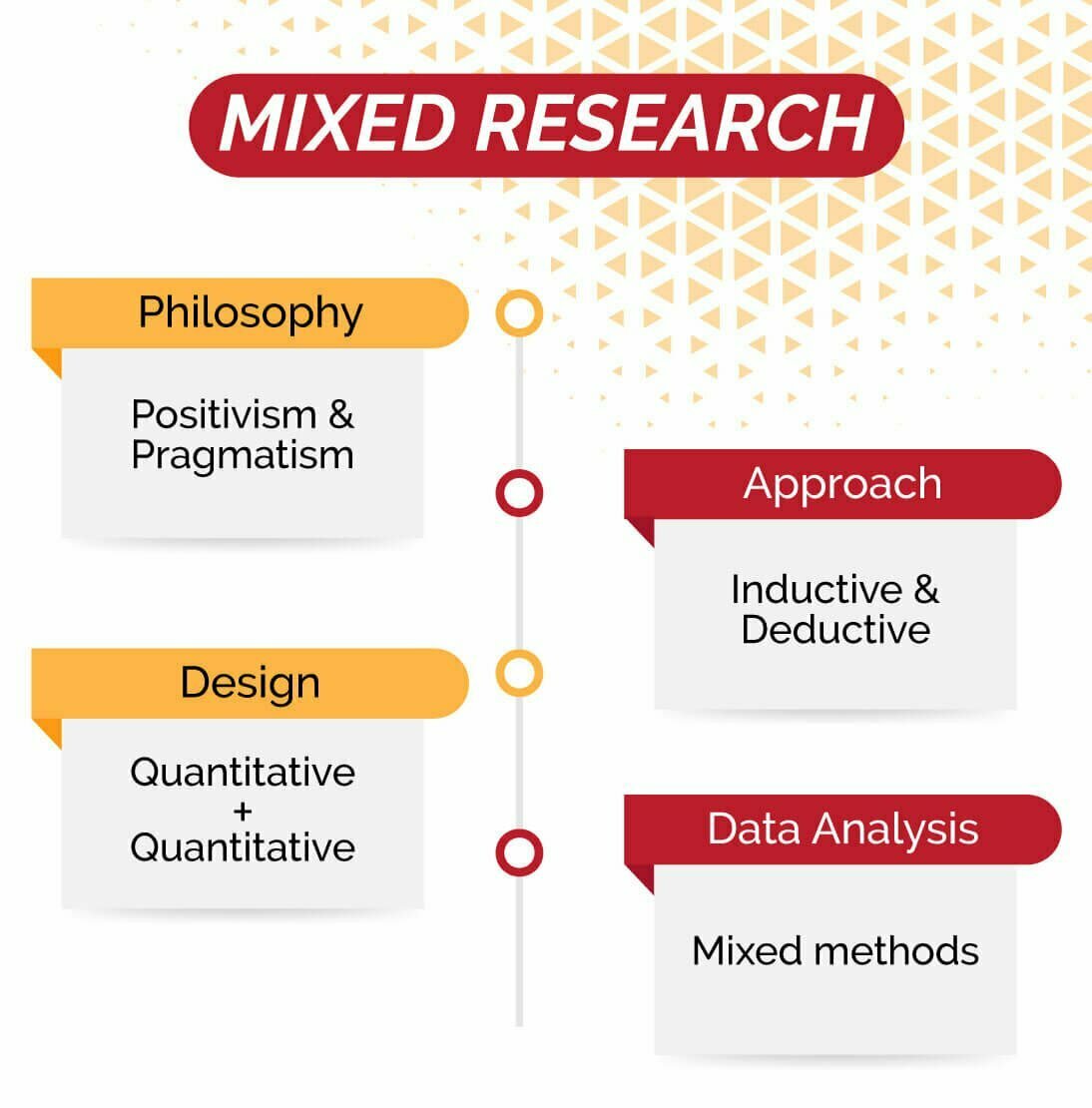
Mixed Data
Mixed data is used when quantitative and qualitative both methods are used in a research. Your topic identifies the research type. In a mixed research a topic could be
“To Analyse The Impact Of Plain Folk Advertising Techniques On Family Shopping
Behaviour Of Consumers: A Case Of Asda Uk”
Here the topic talks about both analysis and impact therefore it is important that a mixed research method is followed. This could be collection of surveys and also taking interviews to test the results of those surveys or vice versa. In a mixed approach data collection methods of quantitative and qualitative are combined.
Data Collection Methods
Just like qualitative and quantitative data can differ so can their methods. Quantitative data collection methods include objective measurements and statistical data analysis. This mostly revolves around numbers and quantifiable data. Quantitative data collection methods include surveys and experiments.
Qualitative data collection methods include observational measurement and visual analysis and mostly depends on non-quantifiable elements. Qualitative data collection methods include interviews with open ended questions and focus groups.
What data type you should use?
Choosing a research method and data type solely depends on the guidelines and requirements you have been provided with from your institute. If your institution requires you to study “the effect of prices on brand switching behavior” you will have to opt for a quantitative study to test the impact of prices on switching behavior and to test the dependency of switching behavior on prices.
When to use quantitative data?
Quantitative data should be used when a researcher is trying to quantify an issue, like we discussed in the example above. The effect on prices on brand switching behavior needs to be quantified.
When to use qualitative data?
Qualitative data should be used when a hypothesis is being developed for further testing or when non-quantifiable factors like emotions and feelings have to be tested.
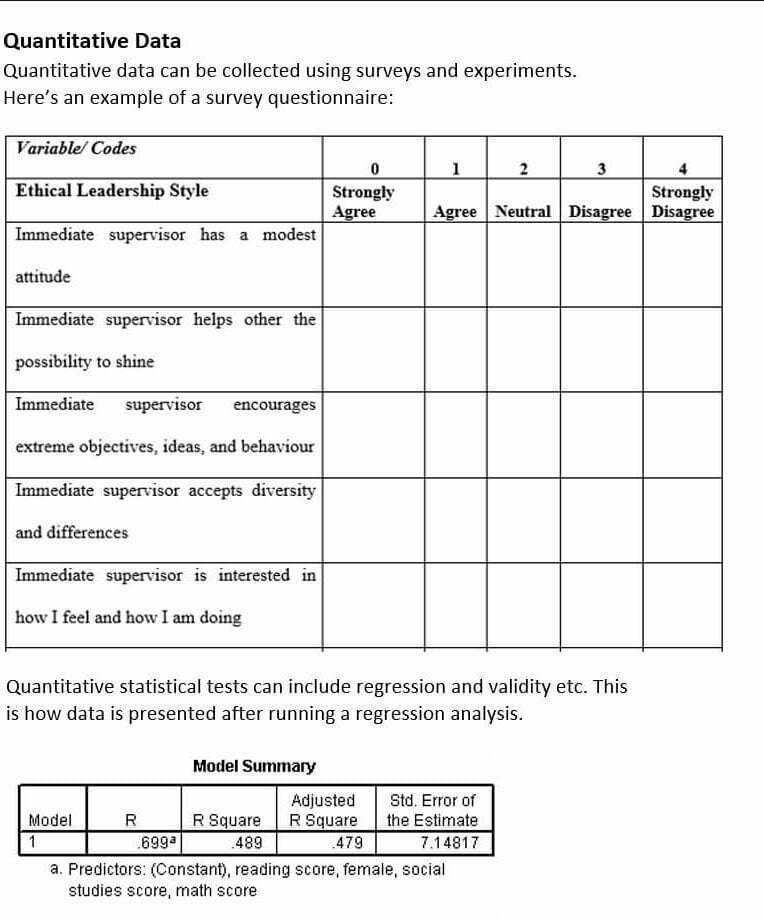
Sample Data
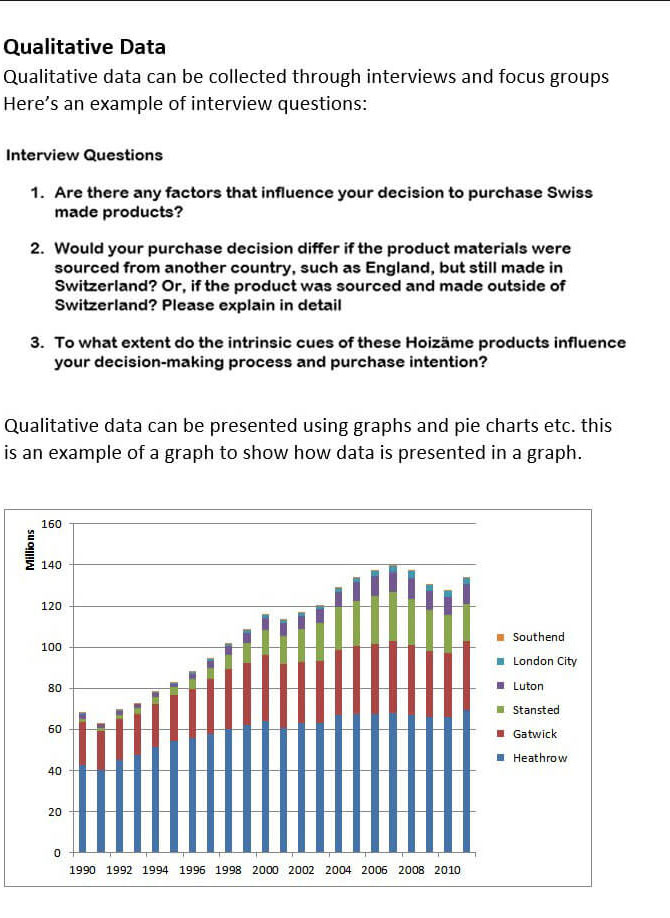
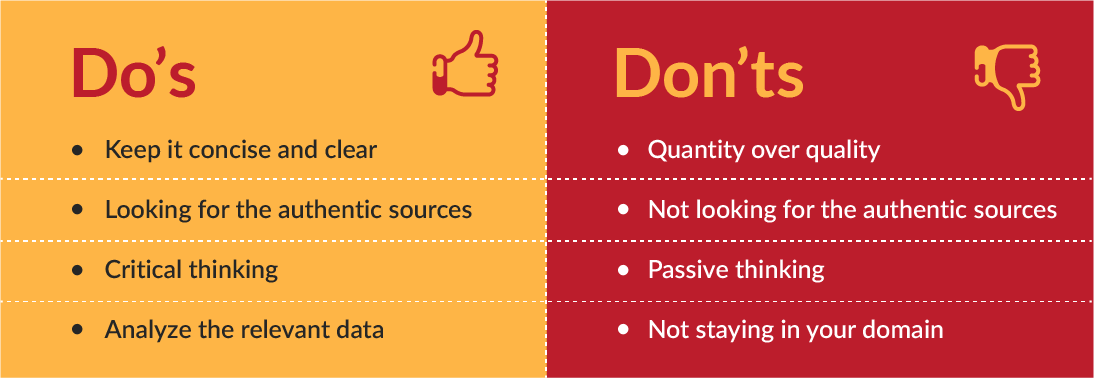
Dos and Don’ts
Here are some dos and don’ts to follow while collecting data.

Now that we have all relevant information we can figure out what data type is required for the topic we initially discussed. Were you able to figure it out? Since we are talking about a relationship between two variables we will have to test their impact and dependency on each other therefore making it a quantitative research. Since it’s a quantitative research quantitative data will be gathered and analyzed.
Free presentation slides
If you are a course instructor willing to educate your class or a student who wants to learn then refer to our free presentation slides available for Google slides and Microsoft PowerPoint.
Meet Dr. Sara Nathan
I am Dr. Sara Nathan and I have done a Ph.D. in aviation management. I have experience of 10 years in mentoring UK’s Students. Over this decade. I enjoy being able to help researchers all around the world as imparting valuable information has always been my passion. Writing & Reading are my passions. For detail about me and to read my other blog you can visit my profile: